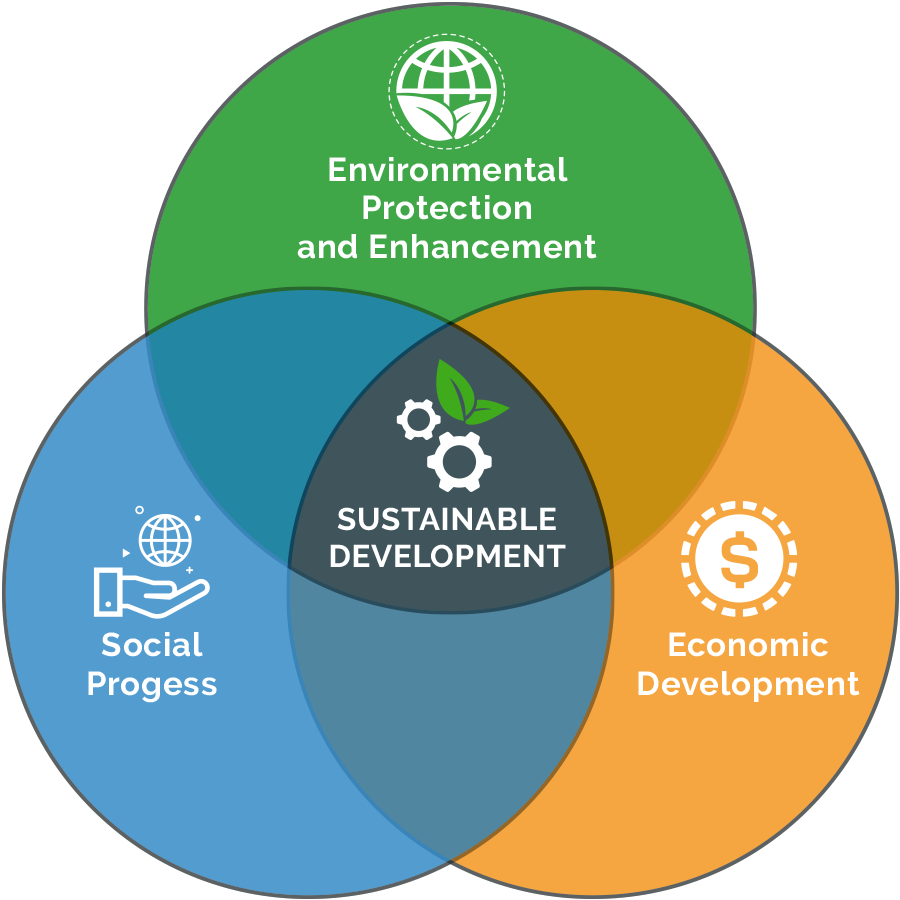
Sustainable Development:
Building a Better Future Without Compromise
Sustainable development is a development approach that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Coined and popularized by the Brundtland Commission in 1987, the concept integrates economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection—often called the three pillars of sustainability. In a world facing climate change, biodiversity loss, and widening inequalities, sustainable development is not just an option; it is a necessity.


The Three Pillars of Sustainable Development
ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
Environmental sustainability focuses on protecting natural resources and ecosystems while ensuring that development activities do not cause irreversible damage. This includes conserving biodiversity, reducing pollution, using renewable energy, and managing waste responsibly.
KEY PRACTICES
Transition to renewable energy (solar, wind, hydro)
Conservation of forests, water bodies, and wildlife
Promoting circular economy and recycling
Reducing carbon emissions and pollution
ECONOMIC SUSTAINABILITY
Economic sustainability aims to support long-term economic growth without negatively impacting social or environmental systems. It encourages efficient resource use, innovation, green jobs, and inclusive economic opportunities.
KEY PRACTICES
Green industries and sustainable businesses
Responsible production and consumption
Long-term planning and investment
Fair trade and ethical supply chains
SOCIAL SUSTAINABILITY
Social sustainability emphasizes equity, inclusion, and the well-being of all people. It focuses on access to education, healthcare, gender equality, decent work, and social justice.
KEY PRACTICES
Quality education and skill development
Gender equality and empowerment
Access to healthcare and sanitation
Community participation and social justice
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS [ SDGs]
WHAT IS SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT?
In 2015, the United Nations adopted the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. These goals provide a comprehensive and universal framework to guide countries, organizations, and individuals toward a more sustainable future. The SDGs aim to balance economic growth, social well-being, and environmental protection.
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals
- No Poverty – End poverty in all its forms everywhere
- Zero Hunger – End hunger, achieve food security, and promote sustainable agriculture
- Good Health and Well-being – Ensure healthy lives for all
- Quality Education – Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education
- Gender Equality – Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
- Clean Water and Sanitation – Ensure availability and sustainable management of water
- Affordable and Clean Energy – Access to reliable, sustainable, and modern energy
- Decent Work and Economic Growth – Promote sustained and inclusive economic growth
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure – Build resilient infrastructure and foster innovation
- Reduced Inequalities – Reduce inequality within and among countries
- Sustainable Cities and Communities – Make cities inclusive, safe, and sustainable
- Responsible Consumption and Production – Ensure sustainable consumption patterns
- Climate Action – Take urgent action to combat climate change
- Life Below Water – Conserve and sustainably use oceans and marine resources
- Life on Land – Protect terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity
- Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions – Promote peaceful and inclusive societies
- Partnerships for the Goals – Strengthen global partnerships for sustainable development

Importance of Sustainable Development
Sustainable development ensures that economic progress does not come at the cost of environmental degradation or social injustice. Its importance can be understood through the following points:
Environmental protection: Preserves ecosystems and biodiversity for future generations
Economic stability: Promotes long-term growth and green innovation
Social equity: Reduces poverty and inequality
Resilience: Helps societies adapt to climate change and global crises

Role of Individuals in Sustainable Development
Every individual has a role to play in achieving sustainability. Small daily actions can collectively create a large impact.
What individuals can do:
Save energy and water
Reduce, reuse, and recycle
Choose sustainable products
Use public transport or cycle
Support eco-friendly brands

Role of Government and Businesses
Governments and businesses are key drivers of sustainable development through policy-making, innovation, and investment.
Government actions:
Environmental laws and regulations
Renewable energy policies
Sustainable urban planning
Social welfare programs
Business actions:
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Sustainable supply chains
Eco-friendly product design
Transparency and ethical practices
Challenges to Sustainable Development
Despite its importance, sustainable development faces several challenges:
Rapid population growth
Climate change and environmental degradation
Lack of awareness and education
Economic inequality
Resistance to policy changes
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, innovation, and strong political will.
Christmas Celebration
Christmas is a global festival on December 25th celebrating Jesus Christ’s birth, marked by religious observance and cultural traditions like decorating trees, exchanging gifts, festive meals, singing carols, and festive lights, blending Christian faith with widespread secular joy and commercial activity, often starting weeks before and continuing through.
Key Aspects of Celebration:
Santa Claus: The figure of Santa Claus (St. Nicholas) brings gifts, a beloved part of the modern tradition
Religious Significance: For Christians, it commemorates the birth of Jesus, the Son of God, often involving church services.
Cultural Traditions: Secular celebrations focus on family, community, and festive cheer.
Decorations: Homes are adorned with Christmas trees, lights, ornaments, and nativity scenes.
Gift-Giving: A major tradition, symbolizing the gifts of the Magi, involves exchanging presents with family and friends.
Festive Foods & Carols: Special meals, drinks, and traditional Christmas carols are common.